
content personalization
What is content personalization?
Content personalization is a branding and marketing strategy in which webpages, email and other forms of content are tailored to match the characteristics, preferences or behaviors of individual users.
Data is crucial to support organizations' personalization strategies. With relevant and updated data, companies can better understand their visitors and customers and use this understanding to create personalized content. This content can potentially boost user satisfaction, improve customer experiences and increase the probability of lead and purchase conversions.
Frequently used for sales, marketing, customer service and e-commerce sales, personalization is sometimes known as one-to-one marketing, because customer-facing content can be and often is tailored to specifically target individual customers or leads.
At a high level, content personalization is about tailoring content to individuals in order to enhance the brand's relationship with them. Personalization also provides a way to create a segment of one, which can meet an individual's needs more effectively and efficiently, while enhancing customer satisfaction and increasing the likelihood of repeat visits and repeat sales.
Examples of personalized content include the following:
- interactive quizzes
- emails
- retargeted ads
- e-commerce recommendations
- gamified apps
E-commerce provides a great example of content personalization. Suppose a customer purchases a book from Amazon. The next time they visit Amazon's website or use its app, they might see a list of recommended products that Amazon thinks the customer might like. These recommendations may be for other books by the same author or books purchased by other people who also bought the book that the customer purchased. Either way, the content is personalized for that customer and presented to them based on their unique purchasing history.
The personalization strategy is also common on websites. Many sites allow visitors to customize pages per their interests or content needs. For example, they may be able to select news categories, local weather reports, local news stories, etc. to personalize their site visit and experience.
What are the benefits of personalization for customers and brands?
Content personalization benefits both customers and brands. Informative, relevant and tailored content on a website or in an email makes customers feel valued. They also feel that the company has invested time and effort in understanding them and creating content they would find useful. These emotions go a long way toward enhancing their experiences with the brand. Great customer experiences (CX) play a vital role in strengthening customer-brand relationships.

In addition, personalized content that aligns with their specific preferences and unique needs (or wants) encourages customers to spend more time and money on a company's products or services. Thus, it can boost an organization's sales and revenues. In the long term, it can garner customer loyalty and trust, and increase the likelihood that the brand will achieve preferred status in its customers' hearts, minds and wallets.
What is the role of data in content personalization?
Content personalization strategies rely on data. Information about potential and existing customers enables organizations to understand who they are, what they have purchased in the past and what their current wants and needs are. They can also understand customers' or users' interests and motivations. These insights enable them to design personalized content and provide individualized and memorable experiences, leading to higher conversions, more sales and greater brand affinity.
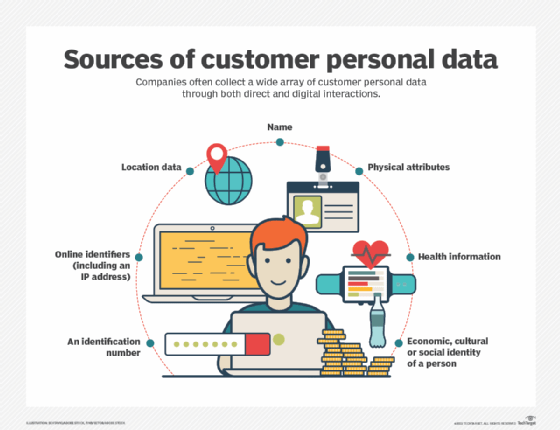
Customer data collected to provide personalized content and experiences may include, but is not limited to the following:
- age or age range
- geographic location
- job title, industry
- previous search queries
- web browsing history
- time and frequency of visits
- device and operating system type
- referring URL (if any)
- session behavior history (e.g., clicks, page views)
- customer lifecycle stage
What are some content personalization methods?
Overall, there are three primary methods of content personalization.
1. Demographic content personalization
Demographic personalization means segmenting a target audience based on demographic and/or behavioral factors and creating content that is personalized for each of those segments. So, a company may segment its audience based on age, geography or gender. They may also create segments based on other factors, such as the following:
- languages known
- job titles
- type of device used
- past brand interactions
Demographic segmentation and personalization can increase the relevance of targeted content for specific groups of users. However, since the content is personalized only at a segment level, the method does not provide a high degree of individual-level personalization.
2. Persona-based content personalization
This method is about creating comprehensive user personas based on specific behaviors and attributes. These personas tell a company what their target customers look like, how they behave and why they shop.
Unlike demographic personalization, persona-based personalization goes deeper than simple segment-level demographics. It also involves identifying and understanding a user's purchase drivers and challenges, and their role in making purchasing decisions. Such understanding enables brands to connect with their audiences at a more personal level and meet their needs more effectively, which can impact their conversions, sales and revenue numbers.
3. Buyer journey-based personalization
In this personalization approach, organizations create maps that visually show where their users are in the sales funnel. These maps enable them to create and deliver personalized appropriate content based on the buyer's journey stage.
For example, a user that lands on a company's website for the first time may be in the awareness stage. This is when they are looking for information to guide their purchase decision. At this point, the business could share content in the form of a blog post or product how-to video that will help the user understand the business and its offerings and move on from the awareness to the purchase stage.
Individual-specific content personalization
By leveraging advances in big data and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, brands can now deliver content that is personalized at the individual level. Individual-specific content personalization has become fairly common in email marketing.
Email marketers can choose from many email service providers like Salesforce Marketing Cloud, MailChimp, HubSpot, etc. to create and deliver content that is unique and personalized to the demographics, needs and purchase history of each individual subscriber.
Emails with the subscriber's name in the subject line and greeting are already quite widespread. Many brands also personalize send times, calls to action (CTA), text and even marketing and advertising copy. Some add dynamic content to their messages that changes depending on the subscriber. In this way, they can send emails with content tailored to each recipient's needs, behaviors and interests instead of sending generic email blasts (also known as spray-and-pray email marketing).
What are content personalization tools?
Marketers and brand managers can choose from many tools to create and deliver personalized content to their target audience. This content can be on their website, app, email, popup forms, landing pages, etc. Some tools can deliver personalized content for the entire customer journey.
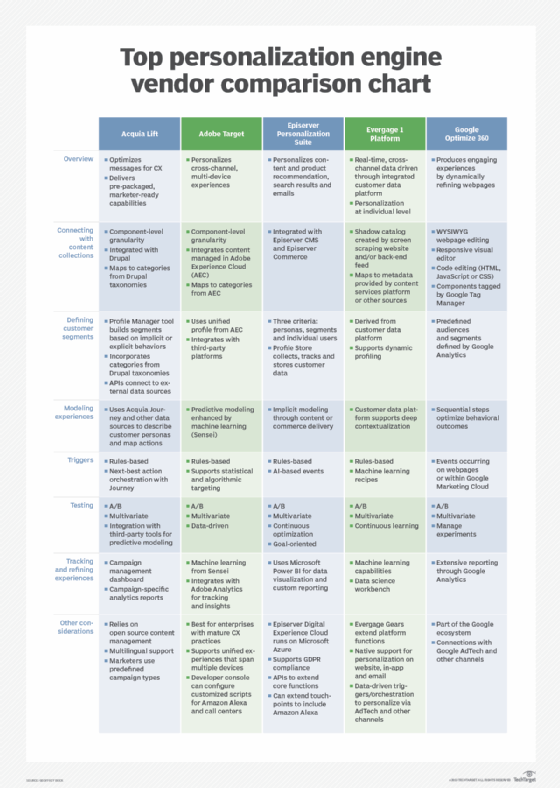
All these tools are data-driven. They work by collecting, aggregating and identifying trends about consumer data. Some tools are customer data platforms (CDPs) while others are personalization engines.
Examples of content personalization tools include the following:
- HubSpot
- Optin Monster
- Moosend
- Yusp
- Episerver
- Evergage
- Qubit
- Sailthru
- Bronto
In addition to personalization software, organizations use web cookies to deliver personalized content to website visitors. Other useful technologies in a firm's personalization toolkit include the following:
- Collaborative filtering. A filter is applied to information from different sites to select relevant data that may apply to a customer's (or customer group's) e-commerce experience.
- User profiling. Data is collected from many sources to create a personalized webpage or landing page before the user has been converted to a customer.
- Data analysis tools. They enable organizations to capture past data and use its insights to predict likely future interactions with a customer or group of customers in the target audience.
Real-world examples of content personalization
Spotify, Netflix and Amazon are all well-known for delivering personalized content to their users.
- Spotify makes song, artist and album recommendations based on the user's past listening history, engagement behavior patterns and what other similar user personas are listening to.
- Netflix's recommendation engine uses data about viewing history, user interactions, title information, duration of user sessions and device type to recommend new shows or TVs to users.
- Amazon generates product recommendations from page views, purchase history and other behavioral data. Users can see these recommendations on both Amazon's website and app.






